[Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] How to Treat Recurrent Rhinitis
Release time: 27 Jan 2026 Author:Shrek
Is your nose "out of control" in winter? Don't let rhinitis accompany you through the winter!
"My nose feels like it's been 'sealed' in winter; I can only breathe through my mouth at night..."
"I wanted to air out the blankets while the weather was nice, but I couldn't stop sneezing..." When cold air becomes an uninvited guest to the respiratory tract, and when heated rooms become "dehydration chambers" for the nasal mucosa, countless people's nasal cavities are undergoing a "seasonal battle."
Morning nasal congestion, constant sneezing during seasonal changes, and medication only providing temporary relief—this is the daily routine for countless rhinitis sufferers. As a common and frequently occurring clinical disease, rhinitis not only obstructs breathing but can also affect the cardiovascular system, seriously impacting sleep, work, and quality of life.
If conventional drug treatment is ineffective, our hospital's ultrasound-guided sphenopalatine ganglion block is helping many rhinitis patients break free from the "breathing shackles."
Reasons why rhinitis "crashes" in winter.
1. Cold air stimulation: Cold, dry air in winter irritates the nasal mucosa, causing blood vessels to constrict and weakening their function, thus triggering inflammation.
2.Drastic temperature changes: Large temperature differences make it difficult for the nasal mucosa to adapt, thus inducing or aggravating rhinitis symptoms, especially vasomotor rhinitis.
3.Allergen accumulation: In winter, closed doors and windows lead to poor indoor air circulation. This creates conditions for the growth of allergens such as dust mites and mold.
4. Fluctuations in immunity: In winter, the body's immunity is relatively low, making people more susceptible to colds. Viral infections can damage the integrity of the nasal mucosa, inducing or aggravating rhinitis.
How to treat allergic rhinitis?
Treatment of allergic rhinitis emphasizes a "prevention and treatment combined, four-in-one" approach, including environmental control, medication, immunotherapy, and health education. Simply put, once the allergen is identified, exposure should be avoided or minimized. Treatment is divided into etiological treatment and symptomatic treatment. Etiological treatment, also known as immunotherapy or desensitization therapy, is the primary approach. Symptomatic treatment includes medication and surgery.
He advises patients to avoid known allergens, such as staying away from pets and using air filtration systems and acaricides in daily life. Medication can quickly, effectively, and safely control nasal symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose, and is currently the main treatment for allergic rhinitis.
How to determine if surgery is necessary for allergic rhinitis?
1. Patients with perennial allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinosinusitis, or nasal polyps (with high eosinophil count) who have shown poor response to 1-2 years of regular drug treatment, or who have poor subjective medication adherence and are unwilling to use medication long-term;
2. Patients with perennial allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinosinusitis, or nasal polyps (with high eosinophil count) complicated by airway hyperresponsiveness or bronchial asthma (abnormal pulmonary function and airway provocation tests);
3. Patients with airway hyperresponsiveness or bronchial asthma complicated by eosinophilic nasal allergic disease;
4. Patients with a history of recurrent nasal polyps surgery (with high eosinophil count), and patients with nasal polyposis (highly likely with a family history, allergic disease, non-allergic asthma, aspirin intolerance, or a history of multiple nasal polyps surgery);
5. Patients who have failed immunotherapy or cannot adhere to long-term immunotherapy;
6. 7. Specific IgE is normal and skin prick test is negative, ingested and inhaled substances are normal, but the patient has significant nasal congestion, nasal obstruction, and nasal hypersecretion (vasomotor rhinitis);
8. Specific IgE is normal and skin prick test is negative, but eosinophils are positive in nasal secretions;
9. Female patients with severe allergic rhinitis who have not responded well to drug treatment and are planning to become pregnant.
How is the surgery performed? What are the risks?
Pterygopterygoid nerve block surgery, by blocking the parasympathetic nerves in the nose, controls the degree of nasal mucosal edema and the secretory state of nasal mucosal glands, and can provide these patients with good clinical efficacy. However, the clinical application of traditional pterygopterygoid nerve block surgery is limited due to postoperative dry eye problems in some patients.
Based on precise anatomical research, the highly selective postganglionic branch block of the pterygoid canal nerve is performed under nasal endoscopy using minimally invasive surgery to precisely block multiple branches of the pterygoid canal nerve that affect nasal and airway functions, while also protecting the lacrimal gland secretory nerves. This approach ensures both definite efficacy and minimizes the risk of complications, making it an effective treatment for the aforementioned patients.
There are many types of rhinitis, and their treatments vary.
Rhinitis presents in various forms. From the perspective of pathological changes in the nasal mucosa, there are chronic simple rhinitis, chronic hypertrophic rhinitis, caseous rhinitis, atrophic rhinitis, etc. From the perspective of the speed of onset and the length of the course, it can be divided into acute rhinitis and chronic rhinitis. In addition, some types of rhinitis, although slow in onset and prolonged in course, have specific causes and therefore specific names, such as allergic rhinitis (i.e., allergic rhinitis) and drug-induced rhinitis.
Minimally invasive treatment is the most thorough, with less trauma and faster recovery. Endoscopic nasal surgery, while thoroughly removing lesions, preserves as much of the normal anatomical structure of the nasal cavity and sinuses as possible, creating good ventilation and drainage, promoting functional recovery, and ultimately achieving the cure of sinusitis and nasal polyps by restoring the physiological functions of the nasal cavity and sinuses themselves, while preventing recurrence. It has the advantages of minimal trauma, less pain during and after surgery, thorough surgery, and precise operation.
Posterior nasal nerve resection is a relatively common clinical treatment method, mainly used to treat allergic rhinitis. The principle of this surgery is to surgically sever the main trunk of the posterior nasal nerve that innervates the turbinates, nasal mucosa, and blood vessels, thereby reducing nerve excitability, alleviating the sensory sensitivity of the nasal mucosa, and reducing or eliminating allergy symptoms.
Who are suitable candidates for posterior nasal nerve resection?
According to ENT specialists, posterior nasal nerve resection is suitable for two groups of people: one is patients with chronic allergic rhinitis who have poor treatment results, cannot use medication long-term, or experience relapse after stopping medication; the other is allergic rhinitis patients who are planning to conceive, because hormonal changes during pregnancy can easily worsen allergic rhinitis, and medication treatment is not possible in early pregnancy. Posterior nasal nerve resection can be performed in the preconception period.
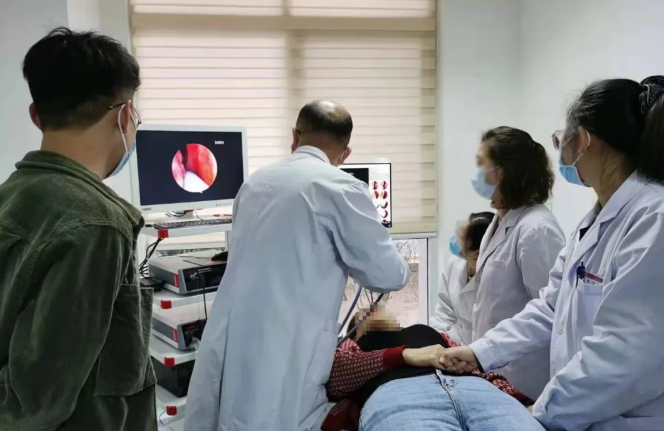
Advantages of Nasal Endoscopy Technology
1. Faster and More Precise Treatment: Nasal endoscopic minimally invasive surgery, through the visual imaging system of the nasal endoscope, can reach deep into hidden areas of the nasal cavity, allowing doctors to have a clear view of the lesion and quickly remove diseased tissue. The entire process is clearly visible, enabling more precise surgery and access to previously inaccessible areas. It transforms traditional destructive surgery into a functional surgery that completely protects the healthy tissues and structures of the nasal cavity.
2.Minimally Invasive and Painless: This minimally invasive surgery requires no incisions in the face or nose; the entire procedure is performed inside the nasal cavity. It offers advantages such as minimal trauma, short operation time, and rapid recovery, without affecting the patient's normal work and life.
3. Superior Safety: Some traditional surgical treatments are not only highly invasive but can also damage the nasal mucosa. Minimally invasive surgery, with its focus on treatment, is non-invasive, more thorough, and safer.
Surgical Indications:
The scope of diagnosis and treatment for nasal endoscopic minimally invasive technology includes: sinusitis, nasal polyps, nasal structural abnormalities, deviated nasal septum, nasal septum perforation, nasal cavity and sinus tumors, etc. Recently, the application of nasal endoscopic surgery has also expanded to include diseases of the orbit, lacrimal duct, and anterior skull base.
Next
没有了!
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] How to Treat Recurrent Rhinitis
- [ENT Surgery: Nasal Endoscopy] Endoscopic Treatment of Nasal Polyps
- [Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] Methods and Precautions for Nasal Bleeding Control under Nasal Endoscopy