【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
Release time: 17 Nov 2021 Author:Shrek
Cholecystectomy is the most common operation in biliary surgery. Since Lengenbuch performed the first cholecystectomy in 1882, it has a history of more than 100 years. In most cases, the operation is relatively standard, and the long-term results after the operation are also satisfactory. Suitable for all kinds of acute and chronic cholecystitis, symptomatic gallbladder stones, gallbladder bulging lesions, etc.
Gallbladder surgery is used to treat gallbladder diseases, mainly cholelithiasis.
The cystic duct is blocked, causing severe abdominal pain-biliary colic.
Infection and inflammation of the gallbladder-cholecystitis.
Obstruct the flow of bile to the duodenum-bile obstruction.
All of the above conditions require cholecystectomy for treatment.
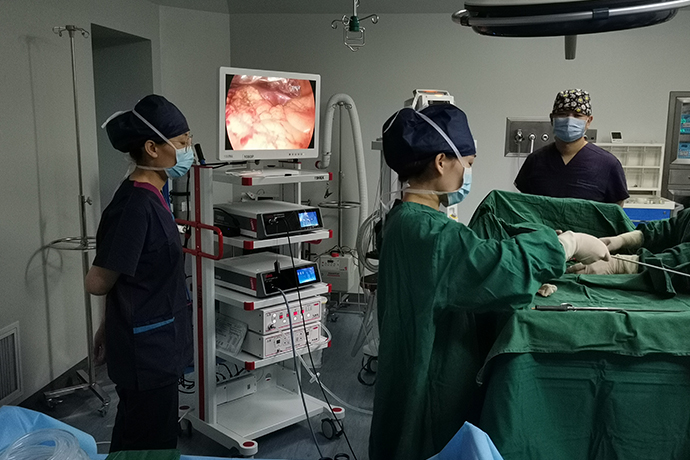
Most gallbladder surgeries have inherited the technology of laparoscopic surgery, using sophisticated instruments including a video camera to enter the abdominal cavity through a small puncture port in the abdomen. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is simple and convenient.
The laparoscopic camera is inserted into the abdominal cavity from near the belly button, and other instruments enter the abdominal cavity through two or more small puncture ports.
After finding the gallbladder, cut off the blood vessels and bile ducts, and then the gallbladder can be taken out.
If the gallbladder is severely infected, inflamed, or has giant gallstones, open the stomach for cholecystectomy. The surgical incision is just under the right abdomen, under the costal arch.
During the operation, the liver is pushed open to expose the gallbladder, the blood vessels and bile ducts connecting the liver and the gallbladder are cut off, the gallbladder is removed, and the common bile duct is checked for obstruction by stones.
If there is a combined infection, a small tube needs to be kept for several days.
Most patients who have undergone laparoscopic cholecystectomy can go home the same day after surgery, and can eat and exercise normally.
Patients who have undergone open cholecystectomy have to stay in the hospital for 5-7 days after surgery, eating normally after a week, and moving normally after 4-6 weeks.
Gallbladder cancer has high level of malignancy, difficult early diagnosis, rapid disease progression, lack of adjuvant treatments, and poor prognosis. Minimally invasive removal of the gallbladder with stones and avoiding canceration of the stones are current practical significance and clinical value.
Regarding gallbladder cancer, the currently identified risk factors include: gallbladder stones, gallbladder adenoma polyps, bile duct cysts, bile duct-pancreatic duct abnormal confluence, long-term chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, such as xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis, porcelain gallbladder, etc. .
Operating skills
Acute operation skills
If gallbladder congestion and edema is obvious and gallbladder tension is high, gallbladder puncture and decompression can be performed first. If the gallbladder wall is thick and cannot be grasped, the gallbladder wall can be cut through electrocoagulation at the neck of the gallbladder, and subserosal peeling starts from the outside of the neck of the gallbladder. , Be careful not to use violence when pulling, find the gap, use aspirator to suck while peeling, move along the wall of the gallbladder to the narrowing part of the neck tube, separate the posterior and anterior triangles of the gallbladder, and continue to freely expose the cystic duct and gallbladder blood vessels. If the stone is trapped in the neck duct of the gallbladder, push the stone toward the gallbladder cavity or remove the stone. If the triangle relationship cannot be distinguished, consider subtotal cholecystectomy.
Operation skills when there is more fat in the gallbladder triangle
When there is a lot of fat in the triangle of the gallbladder, you should close the gallbladder wall and use a suction device to remove the fat tissue for dissection around the gallbladder. Most of the cord-like tissue can be clearly seen. Use small curved separating forceps to pull the cord-like tissue to make a clear distinction. The relationship between the cystic duct and gallbladder blood vessels and the common bile duct, especially the clear exposure of the cystic duct and the transition of the gall bladder neck, is essential for the safety of the operation. After the cystic duct is processed, the distance between the common hepatic duct, the right hepatic duct and the gallbladder wall increases. At this time, it is safer and easier to handle the gallbladder blood vessels close to the gallbladder wall.
Mirizzi syndrome management skills
If there is a greater omentum or organ adhesion around the gallbladder, it is separated close to the gallbladder wall. For those with dense adhesions, it is easier to separate the gallbladder under the serous membrane, and it is not easy to damage the surrounding organs. Then perform the anatomy of the common bile duct and common hepatic duct at the hilar of the liver, and make sure to see its course clearly. When the relationship between the triangle of the gallbladder is clear, an antegrade resection is used. When the relationship is unclear, it is removed by retrograde or combined forward and reverse, and separated by pure separation. It is recommended to use small curved separation forceps for separation, adhere to the principle of not hurting the tube, and can safely and effectively find the gaps between important pipelines. Due to adhesions formed by chronic inflammatory reactions, the gallbladder is atrophy and fibrosis, causing the gallbladder to lose its normal anatomical shape and easy to accidentally injure the CBD. In addition, various pathological conditions can also affect the anatomy and separation of the gallbladder artery, causing difficulty in operation, bleeding and other accidents, so do not force separation during operation.
Bleeding management skills
Full exposure of the surgical field is critical to the operation. When there is more bleeding, the surgeon's restlessness and blind operation are often the main causes of biliary tract injury. It is advisable to use an irrigator to flush the bleeding point, and after the bleeding site is clearly found, compression should be performed to stop the bleeding. If it is bleeding from the broken end of the blood vessel, use the separating forceps to clamp the bleeding point, and slightly pull away from the wound surface for electrocoagulation to reduce the thermal damage to the surrounding tissues. If the gallbladder bed is sheet-like oozing blood, after washing, press the wound surface with a gelatin sponge, while attracting the gelatin sponge, while electrocoagulating the surface, it can effectively stop the bleeding. It is necessary to grasp the principle of accepting what is good, and not excessive electrocoagulation, otherwise the more coagulation, the more bleeding, which may easily cause bile duct damage.
About the application of titanium clip
Excessive use of titanium clips during the operation does not increase the safety of the operation. On the contrary, there are more potential risks, such as falling off and shifting, or even entering the biliary tract, inducing stones and cholangitis. Therefore, the use of titanium clamps should be accurate and appropriate. The titanium clamps have thermal conductivity. The titanium clamps should be avoided during electrocoagulation to avoid unconscious bile duct burns or the titanium clamps falling off.
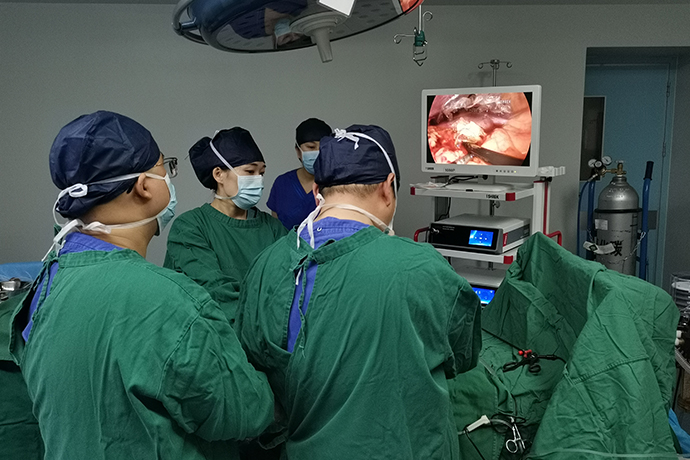
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Urology Cystoscopy Section] Cystoscopic Laser Lithotripsy
- [Laryngoscopy in Otolaryngology] Tonsillectomy
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal