[Percutaneous Nephroscopy in Urology] Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Release time: 24 Sep 2025 Author:Shrek
Due to changes in living habits and dietary structure, the incidence of urinary tract stones in my country is gradually increasing. The best method to treat nephrolithiasis depends on the size, location, composition, hardness and other complications of the stone. Among them, percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is often used for complex kidney stones and some upper ureteral stones.
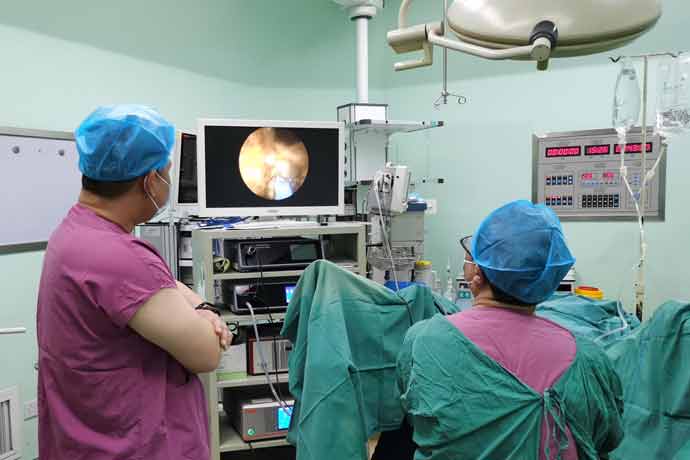
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a technique that uses a lithotripsy device to remove renal pelvic stones, kidney stones, and upper ureteral stones through the created renal fistula tract under direct vision of the nephroscope. PCNL has a high success rate, has the advantages of less pain, quick recovery, wide indications, and few complications.
Preparation of equipment and instruments
Puncture guidance equipment: B-ultrasound or X-ray fluoroscopy machine; Lithotripsy equipment: pneumatic ballistic lithotripsy, ultrasonic lithotripsy, laser lithotripsy, etc.; Pressure perfusion pump: maintain clear vision and flush out the gravel. Imaging system: monitor, camera, cold light source Disinfection: Special instruments of percutaneous nephroscopy are soaked in 2% glutaraldehyde for 10 hours. The camera and B-ultrasound probe are isolated with wire covers.
Preparation of surgical items
1. Endoscopic instruments: 18G sheathed puncture needle, fascial dilator, Peel-away plastic thin sheath, 1 zebra guide wire, ureteroscope, nephroscope, various intraluminal lithotripters (holmium laser, pneumatic ballistic lithotripter), and stone removal forceps. 2. General items: Instrument package: 1 electrosurgical resection package, 1 percutaneous renal special (small handle, tissue scissors, needle holder, toothed forceps, middle curve.)
Other items: 3 wire covers, 1 10ml empty needle, 1 infusion set, 2 brain films, 1 16# urinary catheter, 1 urine bag, 1 drainage bag, 1 No. 5 ureteral catheter, 1 drainage tube and band-aid, 1 irrigation bag. Postural supplies: a set of equipment for lithotomy position and a set of equipment for prone position. 3. Placement of instruments and items: Place the X-ray film on the viewing lamp before surgery;
Various instruments are placed in appropriate positions according to the needs of use: the B-ultrasound machine and imaging system are placed on one side of the operating bed (if the patient has left kidney stones, they are placed on the left side of the bed. It is also the opposite side of the patient's affected side when the patient is in the prone position), the lithotripter and the pressurized perfusion pump are placed on the other side of the bed; the power cords are properly connected to avoid being soaked by the irrigation fluid, and are ready for use after debugging. Open the surgical bag and prepare all the supplies needed for the operation.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy requires many items and equipment, among which special items include a large amount of normal saline, 16-18 g renal puncture needle, f6#~~f18# renal puncture dilator, zebra guide wire, 5# double J tube, 3~5# ureteral catheter, nephrostomy tube, skin peeling sheath, lithotripsy needle, lithotomy forceps, cystoscope, ureteroscope, etc. Special equipment includes pneumatic ballistic lithotripsy, pneumatic perfusion pump, camera system, B-ultrasound machine, etc. All instruments and special items must be placed in place before surgery to ensure the normal operation of the special equipment.
Preoperative psychological guidance
Providing psychological guidance before surgery is of great significance in reducing the incidence of intraoperative and postoperative bleeding and other complications caused by elevated blood pressure caused by psychological factors. The operating room nurse visits the patient in the ward one day before the operation, reads the medical record, and understands the patient's general condition and various routine biochemical examination results. Talk patiently with the patient, dispel the patient's doubts, eliminate nervousness and anxiety, and make the patient confident in the successful completion of the operation.
Indications for percutaneous nephroscopy
All kinds of kidney and upper ureteral stones are indications for percutaneous nephroscopy.
Percutaneous nephroscopy is preferred for the following types: (1) Kidney stones larger than 2.5cm, especially cast stones; (2) Complex kidney stones, symptomatic calyceal diverticulum stones, intrarenal renal pelvis stones with junctional stenosis, etc.; (3) Cystine stones, ESWL-ineffective calcium oxalate stones; upper ureteral or junctional stenosis. Remove foreign bodies from the renal pelvis and upper ureter.
Contraindications of percutaneous nephroscopy
Those with uncorrected systemic hemorrhagic diseases; those with stones combined with ipsilateral renal tumors; those with severe kyphosis of the spine who cannot lie prone; those who are extremely obese and have difficulty establishing a skin-renal passage; those with severe cardiopulmonary disease who cannot tolerate surgery; patients with uncorrected severe diabetes and hypertension.
Cooperation during surgery
Check the performance of each instrument and equipment, connect them correctly, and turn on the power. Connect the camera lens (isolated with a wire cover), cold light source, lithotripsy handle or optical fiber, flushing pipe, etc., turn on the switch, and adjust the lithotripter to the appropriate power. Cooperate with the anesthesiologist to closely observe the patient's vital signs. If there are any abnormalities, promptly notify the operating surgeon. When changing positions during the operation, pay attention to the position of the fistula tube and catheter.
Note: Before the operation, explain to the patient that the prone position will take a long time during the operation. If there is any discomfort, the patient should be informed in time. The success of the operation requires the patient's cooperation so that the patient can be mentally prepared to tolerate this position for a long time. Try to make the patient feel comfortable when in the prone position.
There are many instruments used during the operation, and it is particularly important to arrange their positions appropriately. For example, wires and power cords cannot hinder operation and access, and avoid moisture and conduction of wires. During the operation, the power of the ballistic or holmium laser, the flow rate of the perfusion pump, and the intensity of the light source should be adjusted in advance according to the needs of use.
Intraoperative examination of X-rays will re-check the position of the affected side and prompt the operator. Pay attention to the changes in the patient's condition and place the urine bag in a position that is easy to observe. Since a large amount of irrigation fluid is injected during the operation, more urine is produced, so the urine bag should be opened to avoid reflux.
Adjust the direction of the monitor and the foot pedal position of the lithotripter in a timely manner according to the change of the surgeon's operating position. Add irrigation lotion in time to prevent interruption of water flow from causing unclear surgical field and affecting operation. Keep the patient warm, especially if the operation takes a long time. Pay attention to the protection of the patient's face and eyes.
Familiar with the steps
The general steps of percutaneous nephrolithotomy are as follows:
In the prone position, normal saline is injected retrogradely from the ureteral catheter to cause artificial hydronephrosis. The B-ultrasound machine is used for positioning. A renal puncture is performed in the area between the posterior axillary line and the scapular line under the 11th intercostal space or the 12th rib in a direction perpendicular to the spine to the renal calyx where the stone is located. The zebra guidewire is sent through the puncture needle to the renal calyx, renal pelvis, and ureter, and then under the guidance of the zebra guidewire, a dilator is used to gradually expand from small to large to f18, finally push the F18 dilation tube together with the corresponding peeling sheath into the renal pelvis, pass the ureteroscope into the renal pelvis through the sheath, find the stones, start the water injection pump, use continuous pulses to crush the stones, and finally use the water pressure of the water injection pump to flush out the fine stones or use lithotomy forceps to remove the clean stones, and place the double J tube and F14F16 silicone nephrostomy tube antegrade along the zebra guide wire.
surgical position
After anesthesia, the patient was first placed in the lithotomy position, and an F5 ureteral catheter and urinary catheter were placed. (The ureteral catheter is connected to a saline infusion set suspended at a certain height) The function of the ureteral catheter is:
(1) Water injection increases the pressure in the renal pelvis, which is beneficial to the success of renal puncture; (2) It can be used as a marker to identify the renal pelvis and ureter; (3) Prevents gravel from entering the ureter during lithotripsy; (4) Pressurized water injection through the catheter facilitates the discharge of gravel from the operating sheath. Renal puncture and operating position: prone position, with a narrow soft pillow placed under the abdomen in the kidney area, and the head, chest and lower limbs in a low position.
Postoperative instrument cleaning and maintenance
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy requires many instruments and accessories, some of which are not only expensive but also easily damaged. Therefore, special attention should be paid to cleaning and washed separately. For instruments such as ureteroscopes and stone extraction forceps, pay attention to cleaning the alveoli and keeping the front ends from colliding. When cleaning the endoscope, wipe it with a soft cloth, dry it and apply lubricating oil on the joints for later use. Wipe the camera lens with lens cleaning paper. Equipment used by infected patients should be disposed of separately according to hospital infection requirements.
Nursing experience
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy, as a new technology in urology, is an ideal method for the treatment of kidney stones in recent years. The cooperation of nurses in surgery is a new topic. I have deep experience in the cooperation of 83 cases of percutaneous nephrolithotomy:
1. Be fully familiar with and master the key aspects of surgical methods, surgical positions, surgical safety, precautions and surgical steps, so that you can actively and effectively cooperate with the surgeon during the operation.
2. Be proficient in the correct use, connection methods and precautions of surgical instruments and various instruments. Before surgery, all surgical instruments should be prepared, and special instruments should be checked to see if they are operating normally, such as the performance and functional status of the imaging system; whether the perfusion pump and pipelines are unobstructed and operating normally; and whether the pneumatic ballistic lithotripter is inflated and under pressure.
3. Correct placement and precautions for surgical positions. In the lithotomy position, special attention should be paid to the normal physiological span of the legs apart. After the operation, the limbs should be flattened sequentially, gently, and slowly to avoid fluctuations in vital signs caused by rapid flattening. When the lithotomy position changes to the prone position, nurses, surgeons and anesthesiologists should assist at the same time. First, protect the patient's head, turn the head and body synchronously, use the protruding parts of the clavicle and iliac spinous bones on both sides as fulcrums, put soft pads on, and suspend the chest and abdomen at an appropriate height. At the same time, the affected kidney area should be raised to facilitate surgery and prevent the endotracheal tube from twisting or folding. Finally, check again whether various pipes and indwelling tubes have slipped or shifted.
4. Pay attention to keeping warm and monitoring vital signs during the operation. Since the patients are operated under general anesthesia, a large amount of perfusion fluid is flushed during the operation and the operation is exposed for a long time, and the patient's body temperature will drop. Nurses should take active protective measures to keep the patient's body temperature close to normal and reduce the occurrence of adverse reactions. For example, raise the room temperature to 26°C to 28°C, warm the perfusion solution to 30°C to 35°C, and cover it with multiple layers of surgical drapes during the operation. Extravasation and absorption of perfusion fluid are characteristics of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Large amounts of absorption of perfusion fluid can cause circulatory overload, hyponatremia, metabolic acidosis, etc., which can be life-threatening in severe cases. At the same time, fluid absorption can also cause postoperative non-infectious fever.The factors that affect the absorption of irrigation fluid mainly include perfusion pressure, operation time, surgical technique, etc. Therefore, nurses should take the initiative to carefully and strictly observe the patient's vital signs with the anesthesiologist, pay attention to the color and volume of the irrigation reflux fluid, urine, and adjust the pulse perfusion volume to 200 to 400 ml/min, and the water pressure to 13.5 to 27.0 kpa.
5. Maintenance of surgical instruments Specialist instruments should be managed by dedicated personnel as much as possible, and inspected and repaired regularly to ensure that they will not affect the next operation.
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Urology Cystoscopy Section] Cystoscopic Laser Lithotripsy
- [Laryngoscopy in Otolaryngology] Tonsillectomy
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal