【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Intrahepatic bile duct stones
Release time: 14 Dec 2021 Author:Shrek
Mainly caused by biliary infections and cholestasis
Frequently manifested as abdominal pain, high fever, chills, jaundice and other symptoms. The treatment of intrahepatic bile duct stones is mainly surgery
Early diagnosis and timely treatment are recommended
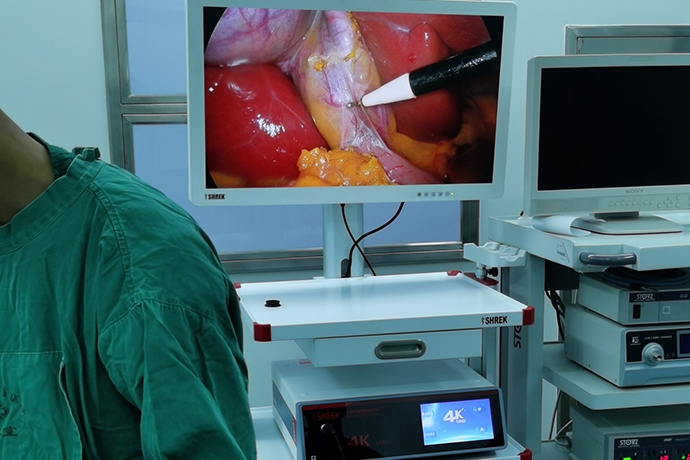
Intrahepatic bile duct stones (Hepatolithiasis) are hepatic bile duct stones, which are stones located above the Y-shaped bifurcation of the left and right hepatic ducts (that is, the stones in the bile ducts above the confluence of the left and right hepatic ducts). The stones are mostly brown or black. Broken, higher bacterial content. The disease is more common in countries in eastern and southern Asia, and is a common disease in some parts of our country.
The most frequently asked questions by patients
Is the stone a stone?
no. Stones do not refer to the stones we see in our lives, but complex calcified deposits formed by the metabolites of various substances in the human body. The main component of intrahepatic bile duct stones is bile pigment stones.
Are intrahepatic bile duct stones easy to remove?
not easy. Hepatolithiasis is prone to residual stones after surgery, and the incidence can reach up to 20%~40%. In recent years, the rate of residual stones after surgery has decreased significantly, but it is difficult to correct some bile duct stenosis and bile duct hemorrhage during stone removal. The reason is that there is still a certain residual rate of postoperative stones.
Can intrahepatic bile duct stones cause bile duct dilation?
Yes. The liver is a digestive organ. The bile secreted by the liver enters the intestine through the bile duct and participates in the digestion and absorption of food. When the bile duct is blocked by stones, the bile cannot be discharged smoothly, and the bile continues to build up, and the increase in pressure will cause the bile duct to dilate.
Will intrahepatic bile duct stones make the liver smaller?
Will do. Due to the obstruction of the stone and repeated stimulation of the accumulated bile, biliary cirrhosis can be caused, which is manifested by a smaller liver and a harder texture.
operation treatment
Minimally invasive surgical treatment of hepatolithiasis includes hepatectomy, choledocholithotomy, and cholangiojejunostomy. The above operations can be done under traditional laparotomy, laparoscopy, or robot-assisted laparoscopy. In principle, the choice of pathological liver resection and/or biliary incision and stone removal is the dominant surgical method.
Liver resection
Under general anesthesia, the doctor removes the diseased liver segment, bile duct, and stones together through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or Da Vinci robot, which is currently a relatively effective treatment method.
Indications: Patients with diseased liver lobe or bile duct stones that are difficult to remove, difficult to correct bile duct stenosis or cystic dilatation, liver parenchymal atrophy and fibrosis, patients with liver abscess or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Bile duct incision and lithotripsy
Under general anesthesia, the doctor cuts the bile duct through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or Da Vinci robot to directly remove the stone or remove the stone with the help of a choledochoscope.
Indications: There is no significant atrophy of the diseased liver segment, no severe stenosis of the bile duct, no residual lesions inside and outside the liver after the stones are removed, and multiple stones in the left and right intrahepatic bile ducts. There is a certain recurrence rate after bile duct incision and stone removal, and some patients may need another operation due to the recurrence of stones.
Bile duct plastic anastomosis
Under general anesthesia, the bile duct will be directly anastomosed and connected to the intestine through laparotomy, laparoscopy or Da Vinci robot, so as to smooth bile drainage. Indications: Patients with intrahepatic bile duct stones and hilar bile duct stenosis, while intrahepatic lesions or bile duct stenosis can be removed. In addition, the loss of Oddi sphincter function, common bile duct cystic dilatation, hilar and extrahepatic bile duct cancer can be considered Application of biliary anastomosis.
Bile duct anastomosis loses the anti-intestinal fluid reflux function of the Oddi sphincter at the lower end of the bile duct. Postoperative complications such as reflux cholangitis, bile duct restenosis, and recurrence of stones, so its surgical indications should be strictly controlled.
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Laryngoscopy in Otolaryngology] Tonsillectomy
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal
- [Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] How to Treat Recurrent Rhinitis