Arthroscopic minimally invasive treatment of "popliteal cyst"
Release time: 02 Aug 2022 Author:Shrek
Arthroscopic minimally invasive treatment of "popliteal cyst" is a leader in China
Popliteal cyst is a general term for synovial cyst in the popliteal fossa, also known as "Baker's cyst", which is a synovial cyst on the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle. It can be divided into two types: congenital and acquired. The former is more common in children, and the latter can be caused by diseases of the bursa itself, such as chronic injury, but some patients are complicated by chronic knee joint disease. The incidence of the elderly is mostly related to knee joint disease and proliferative arthritis.
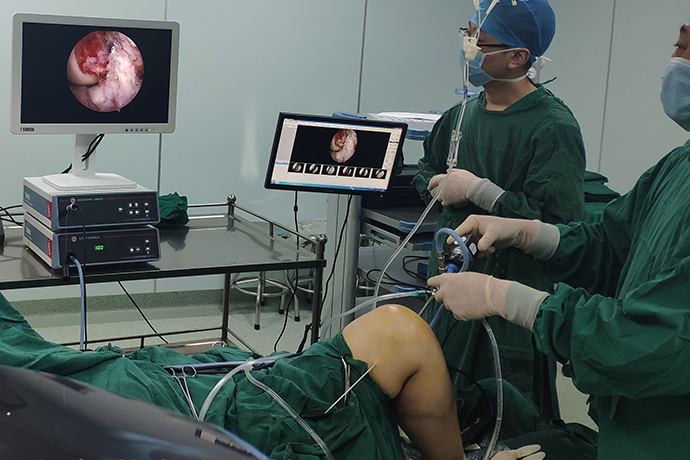
The most common popliteal cysts are the gastrocnemius and semimembranosus tendon bursae, which often communicate with the posterior joint capsule, resulting in limited mechanical extension and flexion of the knee, mild pain, and obvious tension and swelling. Patients often complain of progressive swelling of the popliteal fossa with pain behind the knee. Occasionally a cyst can compress and obstruct venous return, causing edema in the lower leg. Clinically, it is more common in middle-aged and older patients, and the incidence is higher in males than in females.
Causes of popliteal cyst
A correct understanding of the causes of popliteal cysts is very important for how to treat popliteal cysts. Studies have shown that many patients with popliteal cysts have knee osteoarthritis, meniscus damage, cartilage damage, loose bodies, etc. The lesion causes the opening of the synovial sac of the medial head of the gastrocnemius to become a one-way valve, and the synovial fluid can only flow to the synovial sac in one direction, and it is difficult to flow back. cyst. In fact, popliteal cysts occur in up to one in five patients with knee disease.
Therefore, as long as we try to remove the lesions of the knee joint cavity, remove the one-way valve, and open the cyst opening, so that the fluid in the cyst can communicate with the joint cavity, the fluid will not accumulate in the synovial sac, and the cyst will be eliminated naturally.
Clinical symptoms:
Often manifested as vague pain in the back of the knee, local swelling and mass, and tension in the popliteal area. Some patients, especially children, are often asymptomatic and only discovered during physical examination.
Traditional surgical treatment:
Popliteal cysts can be treated by traditional incision, but the trauma is large, the recovery is slow, and the joint function and appearance are seriously affected.
Arthroscopic minimally invasive treatment:
First, through the anterior chamber of the knee joint, it enters the posterior chamber of the knee joint through "between the lateral surface of the medial condyle of the femur and the posterior cruciate ligament". During this process, it will be found that many people have lesions of the meniscus in the joint, which can be treated together.
After entering the posterior compartment of the knee joint, part of the posteromedial joint capsule is first resected.
Then, the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle and the semimembranous tendon were exposed. Between them is the inner mouth of the cyst. In fact, if it is only for the treatment of the popliteal cyst, the basic work of exposing the inner mouth is completed.
In order to be thorough, we entered the joint cavity. There are still several "mouse" hidden in this cavity, and we need to take it away.
The performance after the cyst wall was removed, of course, the mouse has already taken it away, so that the cyst is basically impossible to recur.
Minimally invasive arthroscopic treatment is used, the trauma is small (1cm small mouth), and the recovery is fast.
Arthroscopic minimally invasive treatment can treat intra-articular lesions, open part of the joint capsule to eliminate the one-way valve function to avoid recurrence, and completely remove the capsule wall.
Advantages of arthroscopic minimally invasive treatment of popliteal cyst
1. At the same time of cyst removal, intra-articular lesions are treated to reduce the recurrence rate at the source.
2. Destroy the one-way valve and reduce the recurrence rate in mechanism.
3. Minimally invasive! With several 5mm incisions, postoperative incision complications are greatly reduced and recovery is fast.
After the operation, the patient had almost no pain and could walk on the ground on the second day. He recovered and was discharged from the hospital soon after.
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal
- [Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] How to Treat Recurrent Rhinitis
- [ENT Surgery: Nasal Endoscopy] Endoscopic Treatment of Nasal Polyps