【Otorhinolaryngology Laryngoscopy】Epiglottic Cyst Resection
Release time: 26 Aug 2025 Author:Shrek
Epiglottic cysts refer to cysts that occur under the epiglottis mucosa, and are more common in the epiglottic vallecula, lingual surface of the epiglottis, and the free edge of the epiglottis. There are congenital and acquired epiglottic cysts. Congenital epiglottic cyst is also called laryngeal mucocele. It is caused by the enlargement of the laryngeal sac and is filled with mucus. It is more common in children. There is no specific treatment for this disease, and it mainly relies on surgical resection. The prognosis is good.
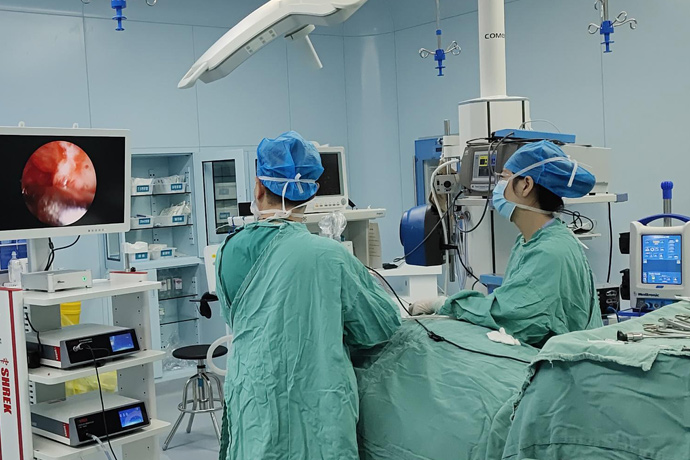
Epiglottic cysts often have no special clinical manifestations in the early stages. They are often found during throat examination. A few large cysts can cause throat discomfort and irritating coughs; congenital large epiglottic cysts can cause laryngeal obstruction symptoms in newborns or infants, and giant cysts in adults can also cause airway obstruction.
Laryngoscopy revealed that the epiglottic cyst was hemispherical, with a wide pedicle, a smooth surface, and was gray-white, light yellow or light red.
Complete resection: Small, superficial cysts
①Fine incision: Carefully incise the mucosa along the edge of the cyst.
②Gradual peeling: Gradually peel off the cyst along the edge of the cyst until the tumor is completely removed. During this process, it is necessary to ensure the accuracy of dissection to avoid damaging surrounding normal tissue.
③ Extracystic wall resection: Try to perform extracystic wall resection during resection to minimize the risk of recurrence. At the same time, resection of too much extracapsular surrounding tissue should be avoided to avoid unnecessary damage.
"Uncovering method": Larger and deeper cysts
① Incise the mucosa and cyst wall: Incise the mucosa from the bulge of the cyst, and continue to incise the cyst wall to aspirate the cyst fluid and expose the cyst cavity
②Remove the lateral wall of the cyst: According to the scope of the cyst, try to remove the lateral wall of the cyst. During resection, it is necessary to ensure that the cyst wall is completely removed, and the resection range must exceed the maximum diameter of the cyst to reduce the risk of recurrence.
③ Bottom wall treatment: The bottom wall of the cyst can be treated with a plasma electrode to further reduce the possibility of recurrence.
④Perichondrium separation: When the cyst wall and the epiglottis cartilage are closely adjacent, interperichondrium separation is required. During this procedure, the plasma electrode should be resected toward the cyst wall side to avoid damaging the epiglottic cartilage.
⑤ Residual mucosal dissection: Combined with laryngeal microinstruments, the remaining mucosa on the cyst wall is peeled off to minimize the risk of recurrence.
Regardless of the complete resection or uncovering method, care should be taken that the power should not be too high and the local contact time should not be too long to avoid damaging the epiglottis and causing perforation or necrosis.
Difficulties of surgery
Difficulty in cyst exposure: Clear exposure of the cyst wall is the key to successful surgery. For patients with obesity, short neck, thick tongue, or reduced neck mobility due to cervical spondylosis, and anteverted Adam's apple, it is more difficult to expose the cyst with an opener or supporting laryngoscope during the operation. A nasal endoscope with a certain angle of the scope can be used to observe the cyst.
If the patient's tongue is too thick and the cyst cannot be exposed by adjusting the length of the tongue depressor, the tongue forceps can be used to pull the tongue out of the mouth, and then the cyst can be exposed by using the mouth opener.
Postoperative treatment
1. Same as general post-operative care under general anesthesia.
2. Regularly atomize and inhale saline containing gentamicin and dexamethasone to dilute sticky phlegm, promote secretion discharge, reduce swelling and reduce inflammation.
3. You can be discharged from the hospital 2 to 3 days after surgery.
4. Rest your voice for 1 week to reduce vocal cord friction. However, you should take more deep breaths to prevent anterior joint adhesion.
5. If there is abrasion on the pharyngeal mucosa, you can use lozenges, gargles and other medicines.
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Urology Cystoscopy Section] Cystoscopic Laser Lithotripsy
- [Laryngoscopy in Otolaryngology] Tonsillectomy
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal