[Laparoscopic Hepatobiliary Surgery] Partial Pancreatectomy
Release time: 28 Feb 2023 Author:Shrek
Overview
Pancreatitis is one of the diseases frequently seen clinically. It is damage caused by the digestion of pancreatic tissue by its own trypsin. Severe pancreatic necrosis combined with infection or abscess requires timely surgical treatment.
1. Onset and treatment Under normal circumstances, pancreatic juice will not stimulate the pancreatic tissue, let alone destroy its own pancreatic tissue. In some pathological conditions, such as blockages such as stones and tumors, bile refluxes into the pancreas and penetrates into the pancreatic tissue, causing the pancreas itself to be digested and causing inflammation of the pancreas. After overeating, most patients suddenly develop obvious abdominal pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting, sometimes fever, and in severe cases, shock symptoms such as pale complexion, cold sweat, weak pulse, and drop in blood pressure.
Mild pancreatitis can be supplemented with body fluids and electrolytes through infusion, relieving spasm and pain, and inhibiting pancreatic secretion. Generally, timely antibiotic treatment is also required. Most of them can be completely cured by this conservative treatment method. In more serious cases of pancreatitis, such as pancreatic abscess with more obvious bad things at the first line, or concurrent infection, or pancreatic pseudocyst, surgical treatment should be performed in a timely manner.
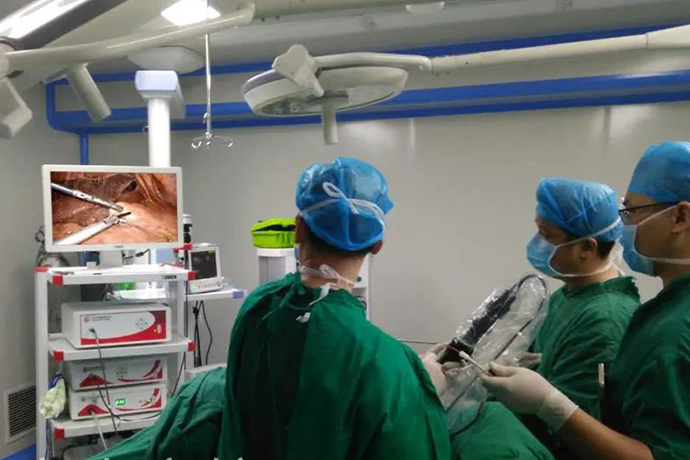
2. Introduction to Surgical Methods
After general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation, the patient was placed in the supine position, and the drape was routinely disinfected. Establish laparoscopic 5 operation holes to start the operation. After the laparoscope enters the abdominal cavity, a comprehensive inspection is first performed to find out whether there is tumor spread in the abdominal cavity, and then the gastrocolic ligament is cut open with an ultrasonic knife to expose the body and tail of the pancreas, and to explore the relationship between the pancreas and the mass and the surrounding tissues. The normal pancreatic tissue on the right side of the tumor was pulled up by the lifting method, and the splenic artery and vein were processed. The pancreas was cut off using an endoscopic cutting stapler (Johnson & Johnson, EC60). The pancreas and spleen were dissected from right to left from the broken end of the pancreas, and the splenocolic ligament and splenorenal ligament were cut off until the whole specimen was dissociated. The resected specimens were put into a laparoscopic bag and taken out around the umbilical cord. After the wound was washed and carefully checked for bleeding, a drainage tube was placed at the pancreatic bed and the incision was closed.
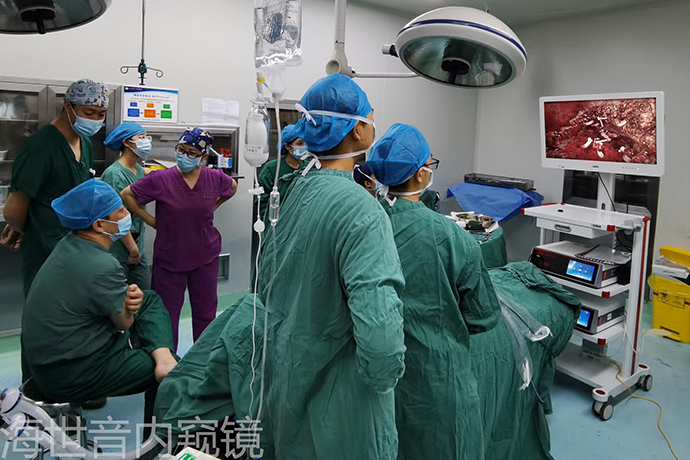
3. Cases
The patient was an elderly woman, 65 years old, who was transferred to the ICU for 4 days mainly due to abdominal pain, which aggravated with chest tightness and shortness of breath for 2 days.
On CT scan, a large liquid dark area around the pancreas can be seen. In consideration of necrotic tissue, puncture and drainage of peripancreatic necrotic tissue was performed under CT guidance. Follow-up 4 days after surgery. The position of the retropancreatic drainage tube was quite good, and the liquid necrotic tissue was reduced. After discussion, it was decided to perform laparoscopic peripancreatic necrotic tissue removal.
Surgical steps:
Establish pneumoperitoneum, enter the stomach, and the peritoneum has been eaten away.
The gastrocolic ligament is opened within the greater curvature of the stomach.
Open the lower edge of the pancreas and find the necrotic tissue.
The debridement technique can be summed up as: lightly gather, slowly twist, wipe and pick again.
Finally, two double sleeves and two ordinary drainage tubes were placed.
Repeat CT was performed 5 days after the operation.
Regardless of whether patients with pancreatitis need surgery or not, they should strictly fast and use a gastric tube for gastrointestinal decompression. After a period of treatment, the abdominal pain disappeared, and there were no other symptoms, and the diet could be gradually resumed. Usually have biliary tract diseases, such as biliary tract stones, cholecystitis and other diseases should be treated early to avoid pancreatitis. Reduce drinking as much as possible, or do not drink. Long-term or heavy drinking can damage organs such as the liver and pancreas. The body’s resistance and anti-infection ability are relatively low. If you suddenly drink a lot of alcohol, it can cause pancreatitis. The diet must be regular and not overeating, otherwise it will lead to gastrointestinal dysfunction and cause pancreatitis.
- Recommended news
- 【General Surgery Laparoscopy】Cholecystectomy
- Surgery Steps of Hysteroscopy for Intrauterine Adhesion
- [Otolaryngology Otoscopic Section] Excision of Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal
- [Otolaryngology Nasal Endoscopy] How to Treat Recurrent Rhinitis
- [ENT Surgery: Nasal Endoscopy] Endoscopic Treatment of Nasal Polyps